Abrasion: различия между версиями
| Строка 10: | Строка 10: | ||
==Пример использования термина на английском языке== | ==Пример использования термина на английском языке== | ||
| − | The collected field data revealed that abrasion of the coast of the continental part is by 2-3 times more intensive than that in the peninsula zone.<ref>Dubra J. Abrasion of the Lithuanian sea coast //2006 IEEE US/EU Baltic International Symposium. – IEEE, 2006. – | + | The collected field data revealed that abrasion of the coast of the continental part is by 2-3 times more intensive than that in the peninsula zone.<ref>Dubra J. Abrasion of the Lithuanian sea coast //2006 IEEE US/EU Baltic International Symposium. – IEEE, 2006. – p. 1-8.</ref> |
Wave refraction and temporal and spatial changes in sediment abrasional and protectional efficacy influence the development of crenulated planforms on coasts with a high degree of geological heterogeneity, and possibly on more geologically homogeneous coasts with longshore variations in cliff height. <ref>Trenhaile А. Rocky coasts ― their role as depositional environments/Earth-Science Reviews ― Volume 159, August 2016, Pages 1-13</ref> | Wave refraction and temporal and spatial changes in sediment abrasional and protectional efficacy influence the development of crenulated planforms on coasts with a high degree of geological heterogeneity, and possibly on more geologically homogeneous coasts with longshore variations in cliff height. <ref>Trenhaile А. Rocky coasts ― their role as depositional environments/Earth-Science Reviews ― Volume 159, August 2016, Pages 1-13</ref> | ||
Текущая версия на 04:55, 26 апреля 2024
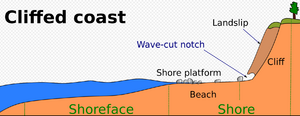
Абразия
Абра́зия — это процесс разрушения берегов водоёма под действием ветровых волн.[1]
Определение на английском
Abrasion is a process of erosion that occurs when material being transported wears away at a surface over time.[2]
Abrasion - рrocess of wearing down by friction, or the resulting effects, with movement of debris, whether it be in a stream, sea, ice or wind.[3]
Пример использования термина на английском языке
The collected field data revealed that abrasion of the coast of the continental part is by 2-3 times more intensive than that in the peninsula zone.[4]
Wave refraction and temporal and spatial changes in sediment abrasional and protectional efficacy influence the development of crenulated planforms on coasts with a high degree of geological heterogeneity, and possibly on more geologically homogeneous coasts with longshore variations in cliff height. [5]
Drift-ice abrasion marks are common along present-day rocky shorelines in cold regions.[6]
Перевод использования на русском языке
Собранные исходные данные показали, что абразия берегов материковой части происходит в 2-3 раза интенсивнее, чем в зоне полуострова.
Преломление волн, временные и пространственные изменения абразионной и защитной эффективности отложений влияют на развитие зубчатых форм на побережьях с высокой степенью геологической неоднородности и, возможно, на более геологически однородных побережьях с вдольбереговыми скалами.
Следы абразии дрейфующего льда часто встречаются вдоль современных скалистых берегов в северных регионах.
Список литературы
- ↑ Чеботарёв А.И. Гидрологический словарь. - Гидрометеорологическое издательство, Ленинград, 1964 г., c. 222
- ↑ Вестгейт, Льюис Г. (февраль 1907 г.). «Абразия ледниками, реками и волнами» . Журнал геологии . 15 (2): 113–120.
- ↑ ВМО, Международный гидрологический словарь, 2013, c.470
- ↑ Dubra J. Abrasion of the Lithuanian sea coast //2006 IEEE US/EU Baltic International Symposium. – IEEE, 2006. – p. 1-8.
- ↑ Trenhaile А. Rocky coasts ― their role as depositional environments/Earth-Science Reviews ― Volume 159, August 2016, Pages 1-13
- ↑ Dionne J-C. Drift-Ice Abrasion Marks along Rocky Shores. Journal of Glaciology. 1985;31(109):237-241. doi:10.3189/S0022143000006560