Bed topography: различия между версиями
Dymasus (обсуждение | вклад) |
Dymasus (обсуждение | вклад) |
||
| (не показаны 2 промежуточные версии этого же участника) | |||
| Строка 1: | Строка 1: | ||
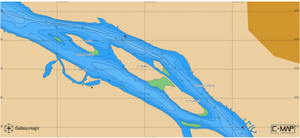
| + | [[Файл:Карта русла реки Ангара.png|мини|Карта рельефа русла реки Ангара (фрагмент)<ref>https://angara.net/forum/t73423 Дата обращения: 21.10.2021</ref>]] | ||
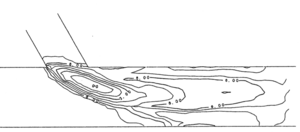
[[Файл:Bed topograhy.png|альт=|мини|300x300пкс|Bed elevation contours show us bed topography<ref>Weerakoon S.B., Tamai N., Kawahara Y. Bed Topography, Bed Shear Stress Distribution and Velocity Field in a Confluence // Proceedings of Hydraulic Engineering. – 1990. – Т. 34. – № October 2017. – P. 307-312. <nowiki>https://doi.org/10.2208/prohe.34.307</nowiki>.</ref> (click to image to increase).<br /><br />]] | [[Файл:Bed topograhy.png|альт=|мини|300x300пкс|Bed elevation contours show us bed topography<ref>Weerakoon S.B., Tamai N., Kawahara Y. Bed Topography, Bed Shear Stress Distribution and Velocity Field in a Confluence // Proceedings of Hydraulic Engineering. – 1990. – Т. 34. – № October 2017. – P. 307-312. <nowiki>https://doi.org/10.2208/prohe.34.307</nowiki>.</ref> (click to image to increase).<br /><br />]] | ||
| Строка 11: | Строка 12: | ||
| − | |||
| + | A simple queueing model which generates '''''bed topography''''' consistent with the mechanics of gravel motion is presented.<ref>Naden P. Modelling gravel‐bed topography from sediment transport // Earth Surface Processes and Landforms. – 1987. – Т. 12. – № 4. – P. 353-367. <nowiki>https://doi.org/10.1002/ESP.3290120403</nowiki>.</ref> | ||
| − | This paper presents a detailed | + | |
| + | This paper presents a detailed assessment of the distributed monitoring and terrain modelling of river '''''bed topography''''' using a technique that combines rigorous analytical photogrammetry with rapid ground survey.<ref>Lane S.N., Richards K.S., Chandler J.H. Developments in monitoring and modelling small‐scale river bed topography // Earth Surface Processes and Landforms. – 1994. – Т. 19. – № 4. – Р. 349-368. <nowiki>https://doi.org/10.1002/ESP.3290190406</nowiki>.</ref> | ||
==Перевод использования на русском языке== | ==Перевод использования на русском языке== | ||
| Строка 20: | Строка 22: | ||
| − | |||
| + | Представлена простая модель, которая генерирует '''''рельеф русла''''' в соотвеnствии с механикой движения наносов в будущем. | ||
| − | В данной статье представлена подробная оценка распределенного мониторинга и моделирования '''''рельефа русла реки''''' с использованием метода, который | + | В данной статье представлена подробная оценка распределенного мониторинга и моделирования '''''рельефа русла реки''''' с использованием метода, который сочетает строгую аналитическую фотограмметрию с быстрым наземным обследованием. |
==Список литературы== | ==Список литературы== | ||
<references responsive="0" /> | <references responsive="0" /> | ||
[[Категория:Русловые процессы]] | [[Категория:Русловые процессы]] | ||
Текущая версия на 09:03, 21 октября 2021
Рельеф речного русла
Это совокупность неровностей поверхности наиболее пониженной части речной долины, выработанной потоком воды.
Определение на английском
Bed topography represents the shape and features of the riverbed. The shape of a riverbed is largely determined by the relief of the terrain through which river crosses. [3]
Пример использования термина на английском языке
Uncertainty in the horizontal location of the aircraft, referred to as the “navigation error”, is an indirect source of error in the altitude of both the surface and bed topography. The error in altitude is the product of the error in horizontal position and the slope of the surface or bed, respectively.[4]
A simple queueing model which generates bed topography consistent with the mechanics of gravel motion is presented.[5]
This paper presents a detailed assessment of the distributed monitoring and terrain modelling of river bed topography using a technique that combines rigorous analytical photogrammetry with rapid ground survey.[6]
Перевод использования на русском языке
Неточность в горизонтальном положении воздушного судна, называемая также "навигационная ошибка" (точнее - тангаж), является косвенным источником погрешности отметок высот, как дневной поверхности, так и рельефа дна. Ошибка в значении высот складывается из ошибки планового положения и наклона дневной поверхности или уклона русла, соответственно.
Представлена простая модель, которая генерирует рельеф русла в соотвеnствии с механикой движения наносов в будущем.
В данной статье представлена подробная оценка распределенного мониторинга и моделирования рельефа русла реки с использованием метода, который сочетает строгую аналитическую фотограмметрию с быстрым наземным обследованием.
Список литературы
- ↑ https://angara.net/forum/t73423 Дата обращения: 21.10.2021
- ↑ Weerakoon S.B., Tamai N., Kawahara Y. Bed Topography, Bed Shear Stress Distribution and Velocity Field in a Confluence // Proceedings of Hydraulic Engineering. – 1990. – Т. 34. – № October 2017. – P. 307-312. https://doi.org/10.2208/prohe.34.307.
- ↑ Kumar V. Bed (Bottom) Topography // Encyclopedia of Snow, Ice and Glaciers / ред. Singh V.P., Singh P., Haritashya U.K. – Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 2011. – P. 93. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-2642-2_38.
- ↑ Hodge S.M., Wright D.L., Bradley J.A., Jacobel R.W., Skou N., Vaughn B. Determination of the surface and bed topography in Central Greenland // Journal of Glaciology. – 1990. – Т. 36. – № 122. – P. 17-30. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022143000005505.
- ↑ Naden P. Modelling gravel‐bed topography from sediment transport // Earth Surface Processes and Landforms. – 1987. – Т. 12. – № 4. – P. 353-367. https://doi.org/10.1002/ESP.3290120403.
- ↑ Lane S.N., Richards K.S., Chandler J.H. Developments in monitoring and modelling small‐scale river bed topography // Earth Surface Processes and Landforms. – 1994. – Т. 19. – № 4. – Р. 349-368. https://doi.org/10.1002/ESP.3290190406.