Debris fan: различия между версиями
(Новая страница: «Файл:111.png|альт=|мини|486x486пкс|Various debris flow fans. (a) The original debris flow fan; (b) Tilcara alluvial fan in Argentina <ref>Marcato...») |
м (→Селевое русло) |
||
| Строка 1: | Строка 1: | ||
| − | [[Файл:111.png|альт=|мини|486x486пкс|Various debris flow fans. (a) The original debris flow fan; (b) Tilcara alluvial fan in Argentina <ref>Marcato | + | [[Файл:111.png|альт=|мини|486x486пкс|Various debris flow fans. (a) The original debris flow fan; (b) Tilcara alluvial fan in Argentina <ref>Marcato G. et al. Debris flood hazard documentation and mitigation on the Tilcara alluvial fan (Quebrada de Humahuaca, Jujuy province, North-West Argentina) //Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences. – 2012. – Vol. 12. – №. 6. – P. 1873-1882.</ref>]] |
==Селевое русло== | ==Селевое русло== | ||
| Строка 8: | Строка 8: | ||
==Пример использования термина на английском языке== | ==Пример использования термина на английском языке== | ||
| − | However, debris fans remain poorly understood due to the lack of sedimentological and stratigraphic data, even though they are not uncommon<ref>Liu | + | However, debris fans remain poorly understood due to the lack of sedimentological and stratigraphic data, even though they are not uncommon<ref>Liu J. et al. Sedimentary architecture of a sub-lacustrine debris fan: Eocene Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, east China //Sedimentary Geology. – 2017. – Vol. 362. – P. 66-82.</ref>. |
==Перевод использования на русском языке== | ==Перевод использования на русском языке== | ||
Текущая версия на 09:17, 26 апреля 2022
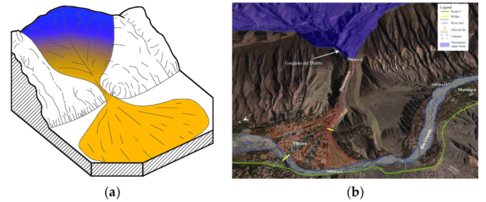
Селевое русло
Русло, по которому проходят селевые потоки с периодичностью, не позволяющей русловому потоку в межселевой период перерабатывать селевые отложения. На крупных горных реках (F > 1000 км2) селевые потоки не формируются, но выносы селевых потоков из притоков, аккумулируясь, создают иногда на значительном их протяжении, изменяя форму продольного профиля, создавая селевые гряды в русле, оказывая большое влияние на направленность и интенсивность русловых деформаций[2]
Определение на английском
A debris fan is a triangular-shaped landform that forms by deposition of material at the intersection of a tributary valley with a larger valley. The material consists of stream-flood sediments and/or mud flow material and is deposited where the stream changes gradient as it enters the larger valley [3].
Пример использования термина на английском языке
However, debris fans remain poorly understood due to the lack of sedimentological and stratigraphic data, even though they are not uncommon[4].
Перевод использования на русском языке
Однако селевые русла остаются плохо изученными из-за отсутствия седиментологических и стратиграфических данных, несмотря на то, что они не являются редкостью.
Список литературы
- ↑ Marcato G. et al. Debris flood hazard documentation and mitigation on the Tilcara alluvial fan (Quebrada de Humahuaca, Jujuy province, North-West Argentina) //Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences. – 2012. – Vol. 12. – №. 6. – P. 1873-1882.
- ↑ Чалов Р. С. Толковый терминологический и понятийный словарь-справчник по русловедению. — Типография "Ваш формат". Москва, 2022. — 142 с.
- ↑ https://coloradogeologicalsurvey.org/hazards/debris-flows/ Accessed 22 April 2022
- ↑ Liu J. et al. Sedimentary architecture of a sub-lacustrine debris fan: Eocene Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, east China //Sedimentary Geology. – 2017. – Vol. 362. – P. 66-82.