Hypolimnion: различия между версиями
Перейти к навигации
Перейти к поиску
| (не показана 1 промежуточная версия этого же участника) | |||
| Строка 7: | Строка 7: | ||
Hypolimnion is the lowest layer in a thermally stratified lake or reservoir. This layer consists of colder, denser water, has a constant temperature, and no mixing occurs<ref>[https://www.owp.csus.edu/glossary/hypolimnion.php https://www.owp.csus.edu/glossary/hypolimnion.php Дата обращения: 12.04.2024 16:53]</ref>. | Hypolimnion is the lowest layer in a thermally stratified lake or reservoir. This layer consists of colder, denser water, has a constant temperature, and no mixing occurs<ref>[https://www.owp.csus.edu/glossary/hypolimnion.php https://www.owp.csus.edu/glossary/hypolimnion.php Дата обращения: 12.04.2024 16:53]</ref>. | ||
| − | Hypolimnion is also described as cooler water below the thermocline in a thermally stratified water body, remote from surface influences and with a relatively flat temperature gradien<ref>World Meteorological Organization (WMO), United Nations Educational S. and C.O. (UNESCO) International Glossary of Hydrology. | + | Hypolimnion is also described as cooler water below the thermocline in a thermally stratified water body, remote from surface influences and with a relatively flat temperature gradien<ref>World Meteorological Organization (WMO), United Nations Educational S. and C.O. (UNESCO) International Glossary of Hydrology. Vol. 471 p. – 3rd ed. – Geneva: WMO; UNESCO, 2012</ref>. |
==Пример использования термина на английском языке== | ==Пример использования термина на английском языке== | ||
| Строка 13: | Строка 13: | ||
# The estimates of the vertical mixing coefficient in the deep hypolimnion are therefore subject to larger errors<ref name=":0">Michalski J., Lemmin U. Dynamics of vertical mixing in the hypolimnion of a deep lake: Lake Geneva // Limnology and Oceanography. 1995. № 4 (40). P. 809–816.</ref>. | # The estimates of the vertical mixing coefficient in the deep hypolimnion are therefore subject to larger errors<ref name=":0">Michalski J., Lemmin U. Dynamics of vertical mixing in the hypolimnion of a deep lake: Lake Geneva // Limnology and Oceanography. 1995. № 4 (40). P. 809–816.</ref>. | ||
# The source of the turbulent mixing in the deep hypolimnion, however, is still unknown<ref name=":1">Lemmin U. Insights into the dynamics of the deep hypolimnion of Lake Geneva as revealed by long-term temperature, oxygen, and current measurements // Limnology and Oceanography. 2020. № 9 (65). P. 2092–2107.</ref>. | # The source of the turbulent mixing in the deep hypolimnion, however, is still unknown<ref name=":1">Lemmin U. Insights into the dynamics of the deep hypolimnion of Lake Geneva as revealed by long-term temperature, oxygen, and current measurements // Limnology and Oceanography. 2020. № 9 (65). P. 2092–2107.</ref>. | ||
| − | # Oxygen depletion in the hypolimnion can also have direct negative effects on benthic invertebrates and fish<ref name=":2">Liboriussen L., et al. Effects of hypolimnetic oxygenation on water quality: Results from five Danish lakes // Hydrobiologia. – 2009. – | + | # Oxygen depletion in the hypolimnion can also have direct negative effects on benthic invertebrates and fish<ref name=":2">Liboriussen L., et al. Effects of hypolimnetic oxygenation on water quality: Results from five Danish lakes // Hydrobiologia. – 2009. – Vol. 625. – № 1. – P. 157-172. </ref>. |
==Перевод использования на русском языке== | ==Перевод использования на русском языке== | ||
| Строка 19: | Строка 19: | ||
# Определение коэффициентов конвективного перемешивания в гиполимнионе подвержено большим погрешностям<ref name=":0" />. | # Определение коэффициентов конвективного перемешивания в гиполимнионе подвержено большим погрешностям<ref name=":0" />. | ||
# Источник турбулентного перемешивания в гиполимнионе, однако, еще не определен<ref name=":1" />. | # Источник турбулентного перемешивания в гиполимнионе, однако, еще не определен<ref name=":1" />. | ||
| − | # Дефицит кислорода в гиполимнионе может оказывать непосредственное негативное | + | # Дефицит кислорода в гиполимнионе может оказывать непосредственное негативное влияние на бентносных беспозвоночных и рыб<ref name=":2" />. |
==Список литературы== | ==Список литературы== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Текущая версия на 23:54, 25 апреля 2024
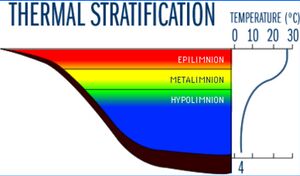
Гиполимнион
Часть водной толщи в стратифицированном водоёме, для которой характерны большая плотность, меньшие изменения температуры по глубине и расположение ниже слоя скачка[1].
Hypolimnion
Hypolimnion is the lowest layer in a thermally stratified lake or reservoir. This layer consists of colder, denser water, has a constant temperature, and no mixing occurs[2].
Hypolimnion is also described as cooler water below the thermocline in a thermally stratified water body, remote from surface influences and with a relatively flat temperature gradien[3].
Пример использования термина на английском языке
- The estimates of the vertical mixing coefficient in the deep hypolimnion are therefore subject to larger errors[4].
- The source of the turbulent mixing in the deep hypolimnion, however, is still unknown[5].
- Oxygen depletion in the hypolimnion can also have direct negative effects on benthic invertebrates and fish[6].
Перевод использования на русском языке
- Определение коэффициентов конвективного перемешивания в гиполимнионе подвержено большим погрешностям[4].
- Источник турбулентного перемешивания в гиполимнионе, однако, еще не определен[5].
- Дефицит кислорода в гиполимнионе может оказывать непосредственное негативное влияние на бентносных беспозвоночных и рыб[6].
Список литературы
- ↑ https://www.ecoindustry.ru/dictionary.html?t=%C3%E8%EF%EE%EB%E8%EC%ED%E8%EE%ED Дата обращения: 12.04.2024 16:49
- ↑ https://www.owp.csus.edu/glossary/hypolimnion.php Дата обращения: 12.04.2024 16:53
- ↑ World Meteorological Organization (WMO), United Nations Educational S. and C.O. (UNESCO) International Glossary of Hydrology. Vol. 471 p. – 3rd ed. – Geneva: WMO; UNESCO, 2012
- ↑ 4,0 4,1 Michalski J., Lemmin U. Dynamics of vertical mixing in the hypolimnion of a deep lake: Lake Geneva // Limnology and Oceanography. 1995. № 4 (40). P. 809–816.
- ↑ 5,0 5,1 Lemmin U. Insights into the dynamics of the deep hypolimnion of Lake Geneva as revealed by long-term temperature, oxygen, and current measurements // Limnology and Oceanography. 2020. № 9 (65). P. 2092–2107.
- ↑ 6,0 6,1 Liboriussen L., et al. Effects of hypolimnetic oxygenation on water quality: Results from five Danish lakes // Hydrobiologia. – 2009. – Vol. 625. – № 1. – P. 157-172.